|
|
| No dimensional drawings!
Unit:
|
|
|
| No dimensional drawings!
Unit:
|
下列定義适用于本标準。
鋅鉻塗層 Zinc / Chromate coatings
将水基鋅鉻塗料浸塗、刷塗或噴塗于鋼鐵零件或構件表面,經烘烤形成的以鱗片狀鋅和鋅的鉻酸鹽為主要成分的無機防腐蝕塗層。
根據鋅鉻塗層的塗敷量和塗層厚度将鋅鉻塗層分成表 1 所示四個級别。
| 分級 | 塗敷量 / (mg/dm²) | 塗層厚度 / μm | 工藝 |
| 1 | 70 | 2 | 一塗一烘 |
| 2 | 160 | 4.6 | 二塗二烘 |
| 3 | 200 | 5.8 | 二塗二烘 |
| 4 | 300 | 8.6 | 三塗三烘 |
| 注:塗敷量是塗層的分級及技術要求的仲裁值,塗層厚度是參考值。表中所列的塗層厚度是根據塗層密度為 3.5 g/cm³ 換算所得。由于塗層中存在是否加入鋁和加入鋁量的多少等因素使得塗層密度不盡相同,所以塗層厚度僅為參考值。當被塗工件形狀複雜,表面積不宜确定時,塗敷量的檢測将會困難,此時可由供需雙方協商,參照塗層厚度對塗層進行分級。 | |||
a) 本标準号;
b) 待塗敷件要求的塗層等級;
c) 待塗敷工件的最終熱處理溫度。由于鋅鉻塗層是在 300℃ 左右的溫度下進行烘烤,需方應考慮該溫度是否影響塗敷工件的力學性能。
不同等級的塗層,經鹽霧試驗後,出現紅鏽的時間不低于表 2 要求。
表 2 耐鹽霧腐蝕試驗要求
| 塗層等級 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| 出現紅鏽時間 / h | 120 | 240 | 480 | 1000 |
8.2.1 溶解稱量法
質量大于 50g 試樣,采用精度為 1 mg 的天平稱得原始質量 W₁ (mg)。将試樣置入 70℃~80℃ 的 20%NaOH 水溶液中,浸泡 10 min,使鋅鉻塗層全部溶解。取出試樣,充分水洗後立即烘幹,再稱取塗層溶解後試樣的質量 W₂ (mg)。量取并計算出工件的表面積 S (dm²),按下列公式計算出塗層的塗敷量 W s ( mg/dm² ):
W s = (W₁ - W₂)/ S
常用零件的塗層表面積計算方法參見附錄A。
注1:若試樣的質量小于 50 g,則應累積若幹件試樣以達到 50 g 以上的質量後,再進行塗敷量試驗。
注2:鋅鉻塗層浸入 NaOH 溶液中溶解 10 min 後,塗層若沒有完全溶解,則應延長浸泡時間,直到塗層完全溶解為止。
8.2.2 金相顯微鏡法
按 GB/T 6462 要求,采用金相顯微鏡法檢測塗層的厚度。
濕熱試驗在濕熱試驗箱中進行,濕熱試驗箱應能調整和控制溫度和濕度。
将濕熱試驗箱溫度設定為 40℃ ± 2℃ , 相對濕度為 95 % ± 3 %,将樣品垂直懸挂于濕熱試驗箱中,樣品不應相互接觸。當濕熱試驗箱達到設定的溫度和濕度時,開始計算試驗時間。連續試驗 48 h 檢查一次,檢查樣品是否出現紅鏽。兩次檢查後,每隔 72 h 檢查一次。每次檢查後,樣品應變換位置。240 h 檢查最後一次。
A.1.1 平墊片
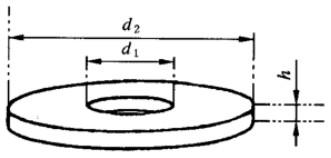 S = [ 1.57(d₁ + d₂ ) (d₂ - d₁ + 2h )] × 1 / 10 000 (dm²)
S = [ 1.57(d₁ + d₂ ) (d₂ - d₁ + 2h )] × 1 / 10 000 (dm²)
A.1.2 彈簧墊片
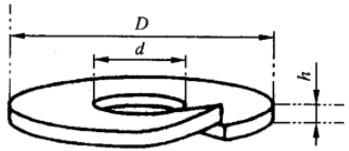 S = [ 1.57(D + d ) (D - d + 2h )] × 1 / 10 000 (dm²)
S = [ 1.57(D + d ) (D - d + 2h )] × 1 / 10 000 (dm²)
A.1.3 六角螺栓
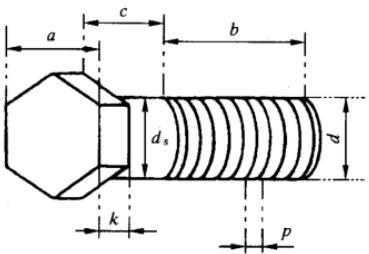 S = [ 1.73( a² + 2 am ) - 1.57d² + m (5.56 d - 3.67 p )] × 1 / 10 000 (dm²)
S = [ 1.73( a² + 2 am ) - 1.57d² + m (5.56 d - 3.67 p )] × 1 / 10 000 (dm²)
A.1.4 六角螺母
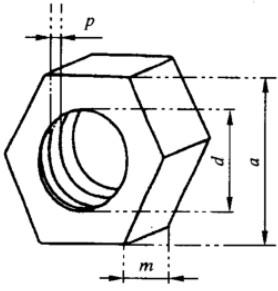 S = [ 1.73( a² + 2 am ) - 1.57d² + m (5.56 d - 3.67 p )] × 1 / 10 000 (dm²)
S = [ 1.73( a² + 2 am ) - 1.57d² + m (5.56 d - 3.67 p )] × 1 / 10 000 (dm²)
A.2.1 分解成簡單形狀計算
将複雜形狀工件的表面分解成若幹個簡單形狀的表面,該複雜形狀工件的表面積等于若幹個簡單形狀的表面積之和。例:
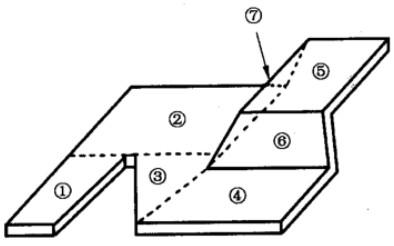 S = S₁ + S₂ + S₃ + S₄ + S₅ + S₆ + S₇
S = S₁ + S₂ + S₃ + S₄ + S₅ + S₆ + S₇
注:S 為複雜形狀工件的表面積。S₁,S₂,S₃,S₄,S₅,S₆ 和 S₇ 分别為圖中 ①、②、③、④、⑤、⑥ 和 ⑦ 等七個簡單表面的表面積。
A.2.2 用坐标紙仿形計算
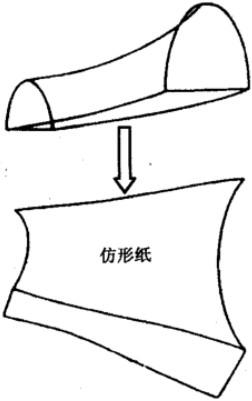

取一張面積為 X ( dm² ) 的坐标紙做标準紙,并稱量其質量為 b(g)。另外取一張坐标紙對被塗工件表面進行仿形。稱量仿形紙的質量為 a (g)。按下式計算出仿形紙的面積即為被塗工件的表面積 S(dm²):
S = a / b * X
鋅鉻塗層是一種高耐蝕塗層,生產過程對環境基本無污染。鋅鉻塗層與電鍍鋅、電鍍镉、熱浸鋅相比,其優點及應用如下。
B.1.1 耐腐蝕性能更好
B.1.2 能适用于多種零件
B.1.3 耐熱性能良好
B.1.4 不會產生氫脆
B.1.5 良好的深塗性能
B.1.6 良好的可塗裝性能
B.1.7 于鋁及其合金不會產生電偶腐蝕
B.1.8 對環境不產生污染
Metallic and other inorganic coatings - Electrodeposited coatings of nickel, nickel plus chromium, copper plus nickel and of copper plus nickel plus chromium
Fasteners - Fundamentals of hydrogen embrittlement in steel fasteners
Metallic coatings - Hot dip galvanized coatings on fabricated iron and steel articles - Specifications and test methods

Fasteners - Hot dip galvanized coatings
Metallic coatings - Electrodeposited coatings of nickel
Chemical conversion coatings - Black oxide coating on iron and steel - Specification and test methods
Chromate conversion coatings on electroplated zinc and cadmium coatings
Metallic coatings - Electroplated coatings of zinc and zinc alloys on iron or steel with supplementary Cr(Vl)-free treatment
Metallic coatings - Hot dip galvanized coatings on fabricated iron and steel articles - Specifications and test methods

Fasteners - Non-electrolytically applied zinc flake coatings systems
Fasteners - Electroplated coating systems
Corrosion of metals and alloys - Corrosivity of atmospheres - Classification, determination and estimation

Fasteners—Hot dip galvanized coatings

Passivation of corrosion-resistant stainless-steel fasteners
Metallic coatings - Electrodeposited coatings of nickel
Chromate conversion coatings on electroplated zinc and cadmium coatings
Metallic coatings - Electroplated coatings of copper plus nickel plus chromium on iron or steel
Metallic and Other Inorganic Coatings - Electroplated Coatings of Zinc with Supplementary Treatments on Iron or Steel
Metallic and other inorganic coatings - Electrodeposited coatings of nickel, nickel plus chromium, copper plus nickel and of copper plus nickel plus chromium
Sherardizing of iron and steel articles
Aerospace series - Electrolytic silver plating of fasteners
Corrosion Protection of Metals - Electrodeposited Coatings of Zinc with Supplementary Treatment on Iron or Steel
Fasteners - surface discontinuities - nuts
Fasteners - Surface Discontinuities - Part 1: Bolts, Screws and Studs for General Requirements
Fasteners - Surface Discontinuities - Part 3: Bolts, Screws and Studs for Special Requirements
Water-based epoxy anticorrosive coatings
Electroplated coatings on threaded components - Part 1: Cadmium on Steel Components - Part 2: Zinc on Steel Components
Selection principle and thickness series for metallic and chemical coating
Specification for electroplated coatings of zinc on iron and steel
General specification for fastener aluminum coating for aircraft
