

2. 表面缺陷的種類、原因、外觀特征和極限
2.1 裂縫 Cracks
裂縫是一種清晰(結晶體)的沿金屬晶粒邊界或橫穿晶粒的斷裂,并可能含有外來元素的夾雜物。裂縫通常是金屬在鍛造或其他成型工序或熱處理的過程中,由于受過高的應力而造成的,也可能在原材料中即存在裂縫。當工件被再次加熱時,通常由于氧化皮的剝落而使裂縫變色。
2.1.1 淬火裂縫 Quench Cracks
原 因 | 在熱處理過程中,由于過高的熱應力和應變,都可能產生淬火裂縫。 淬火裂縫通常是不規則相交、無規律方向的呈現在緊固件表面 |
外 觀 |
|
極 限 | 任何深度、任何長度或任何部位的淬火裂縫都不允許存在。 |
2.1.2 鍛造裂縫Forging cracks
原 因 | 鍛造裂縫可能在切料或鍛造工序中產生,并位于螺栓和螺釘的頭部頂面 |
外 觀 |
|
極 限 | l≤1d; 鍛造裂縫的深度或寬度b: b≤0.04d; 本鍛造裂縫的極限不适用于凹槽頭螺釘(2.1.5條)。 d——螺紋公稱直徑 |
2.1.3 鍛造爆裂Forging bursts
原 因 | 在鍛造過程中可能產生鍛造爆裂,如在螺栓和螺釘六角頭的對角上,或在法蘭面或圓頭產品的圓周上,或在凹穴頭部隆起部分出現 |
外 觀 |
|
極 限 |
六角法蘭面螺栓和螺釘的法蘭面上的鍛造爆裂,不應延伸到頭部頂面的頂圓(倒角圓)或頭下支承面内。對角上的鍛造爆裂,不應使對角寬度減小到低于規定的最小尺寸。 螺栓和螺釘凹穴頭部隆起部分的鍛造爆裂,其寬度不應超過0.06d或深度低于凹穴部分。 圓頭螺栓和螺釘及六角法蘭面螺栓: 螺栓和螺釘的法蘭面和圓頭圓周上的鍛造爆裂不應超過下列極限: 鍛造爆裂的寬度: ≤0.08dc(或dk)(隻有一個鍛造爆裂時); ≤0.04dc(或dk)(有兩個或更多的鍛造爆裂時,其中有一個允許到0.08dc 或dk ) 。 鍛造爆裂的深度: ≤0.04dc d——螺紋公稱直徑;dc——頭部或法蘭直徑; dk——頭部直徑 |
2.1.4 剪切爆裂Shear bursts
原 因 |
剪切爆裂也可能產生在六角頭產品的對邊平面上 |
外 觀 |
|
極 限 |
位于扳擰頭部剪切爆裂的極限: 寬度 ≤ 0.25 mm + O.02s ; 深度 ≤ 0.04d 。 六角法蘭面螺栓和螺釘的法蘭面上的剪切爆裂,不應延伸到頭部頂面的頂圓(倒角圓)或頭下支承面内。對角上的剪切爆裂,不應使對角寬度減小到低于規定的最小尺寸。 螺栓和螺釘凹穴頭部隆起部分的剪切爆裂,其寬度不應超過0.06d或深度低于凹穴部分。 圓頭螺栓和螺釘及六角法蘭面螺栓: 螺栓和螺釘的法蘭面和圓頭圓周上的剪切爆裂的寬度不應超過下列極限: ≤0.08dc(或dk)(隻有一個剪切爆裂時); ≤0.04dc(或dk)(有兩個或更多的剪切爆裂時,其中有一個允許到0.08dc 或dk ) 。 s——對邊寬度;d——螺紋公稱直徑;dc——頭部或法蘭直徑;dk——頭部直徑 |
2.1.5 凹槽頭螺釘的鍛造裂縫Forging cracks socket head screws
原 因 | 在鍛造和加工凹槽的過程中,由于剪切和擠壓應力的作用,可能在圓周、頂面和凹槽(如内六角)等内、外表面上產生裂縫 |
外 觀 |
允許的深度: h1≤O.03dk(最大值為0.13 mm); h2≤0.06dk(最大值為1.6 mm)。
dk——頭部直徑;t——凹槽深度 |
極 限 | 從凹槽内延伸到外表面以及在橫向可能相交的裂縫是不允許的。槽底0.3t範圍内不允許有裂縫。允許位于凹槽其他部位的裂縫,但長度不應超過0.25t,深度不應超過0.03dk(最大值為0.13 mm)。 在頭杆結合處和頭部頂面上,允許有一個深度不超過0.03dk(最大值為0.13 mm)的縱向裂縫。在圓周上允許有深度不超過0.06dk(最大值為1.6 mm)的縱向裂縫。 |
2.2 原材料的裂紋和條痕Row material seams and laps
原材料的裂紋或條痕通常是沿螺紋、光杆或頭部縱向延伸的一條細直線或光滑曲線的缺陷。
原 因 | 裂紋和條痕通常是制造緊固件的原材料中固有的缺陷 |
外 觀 |
|
極 限 |
≤ 0.015d + O.1 mm(最大值為0.4 mm)。 如果裂紋或條痕延伸到頭部,則不應超出對鍛造爆裂規定的寬度和深度的允許極限(2.1.3條)。 d——螺紋公稱直徑 |
2.3 凹痕Voids
凹痕是在鍛造或墩鍛過程中,由于金屬未填滿而呈現在螺栓或螺釘表面上的淺坑或凹陷。
原 因 | 凹痕是由切屑或剪切毛刺或原材料的鏽層造成的痕迹或壓印,并在鍛造或镦鍛工序中未能消除 |
外 觀 |
|
極 限 | h ≤ 0.02d(最大值為0.25 mm)。 凹痕的面積: 支承面上凹痕面積之和,不應超過支承面總面積的5%。 d——螺紋公稱直徑 |
2.4 皺紋Folds
皺紋是在鍛造過程中,呈現在緊固件表面的金屬折疊。
原 因 | 在镦鍛的一次沖擊過程中,由于體積不足和形狀不一造成材料的位移而產生皺紋 |
外 觀 |
|
極 限 |
在外拐角上的皺紋允許存在。 |
2.5 切痕Tool marks
切痕是縱向或圓周方向淺的溝槽。
原 因 | 切痕因制造工具超越螺栓或螺釘表面的運動而產生 |
外 觀 |
|
極 限 | 在光杆、圓角或支承面上,由于加工產生的切痕,其表面粗糙度不應超過Rα=3.2μm(按GB/T 1031規定) |
2.6 螺紋上的折疊Laps on the thread
折疊是螺紋表面的金屬皺紋,通常在各個產品中以相同的式樣出現。也即在同一批產品上,折疊是在相同位置和同樣的移動方向上出現。
原 因 | 在輾制螺紋的冷成型過程中,產生螺紋上的折疊或皺紋 |
外 觀 |
H 1——牙型高度 |
極 限 | 螺紋牙底; 在中徑以下螺紋牙受力側面,即使其起點在中徑以上,也不允許。 下列折疊允許存在: 螺紋牙頂O.25H1範圍内的折疊; 每扣螺紋上在半圈以内的未完全滾壓出的螺紋牙頂; 在中徑以下位于不受力螺紋牙側并向大徑方向延伸的折疊,其深度不大于0.25H1,每扣螺紋上的長度不大于半圈螺紋長度。 H1——牙型高度 |
2.7 損傷Damages
損傷是指螺栓或螺釘任何表面上的刻痕。
原 因 | 損傷,如凹陷、擦傷、缺口和鑿槽,因螺栓或螺釘在制造和運輸過程中受外界影響而產生 |
外 觀 | 沒有準确的幾何形狀、位置或方向,也無法鑒别外部影響的因素 |
極 限 | 位于螺紋最初三扣的凹陷、擦傷、缺口和鑿槽不得影響螺紋通規通過,其擰入時的力矩不應大于0.001d 3 N • m。 如有必要,按特殊協議,如包裝要求,以避免運輸中的損傷。 d——螺紋公稱直徑 |
表1 允許的表面缺陷
條 | 2.1.2 | 2.1.3 | 2.1.4 | 2.1.5 | 2.2 | 2.3 | 2.6 | 2.7 | ||||||
缺陷 | 鍛造裂縫 | 鍛造爆裂 | 剪切爆裂 | 内六角螺釘的裂縫 | 條痕 | 凹痕 | 螺紋上的折疊 | 損傷 | ||||||
螺紋公稱直徑 | 長度 | 寬度和深度 | 圓頭和法蘭頭 | 寬度 | 深度 | 凹槽 | 頭部 | 原材料 | 深度 | 深度 | 扭矩值 | |||
寬度 | 深度 | 長度 | 深度 | 表面深度 | 棱邊 | |||||||||
d | Max | Max | Max | Max | Max | Max | Max | Max | Max | Max | Max | Max | Max | Max |
5 | 5 | 0.2 | 0.08×頭部或法蘭直徑或0.01×頭部或法蘭直徑 | 0.2 | 0.25+0.02s (對扳手面) 0.08×頭部或法蘭面直徑或0.04×頭部或法蘭直徑 | 0.2 | 0.25×凹槽深度 | 0.13 | 0.03×頭部直徑,最大0.13 mm | 0.06×頭部直徑,最大1.6 mm | 0.17 | 0.1 | 0.11 | 0.125 |
6 | 6 | 0.24 | 0.24 | 0.24 | 0.13 | 0.19 | 0.12 | 0.14 | 0.22 | |||||
7 | 7 | 0.28 | 0.28 | 0.28 | 0.13 | 0.21 | 0.14 | 0.14 | 0.33 | |||||
8 | 8 | 0.32 | 0.32 | 0.32 | 0.13 | 0.22 | 0.16 | 0.17 | 0.51 | |||||
10 | 10 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.13 | 0.25 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 1 | |||||
12 | 12 | 0.48 | 0.48 | 0.48 | 0.13 | 0.28 | 0.24 | 0.24 | 1.73 | |||||
14 | 14 | 0.56 | 0.56 | 0.56 | 0.13 | 0.31 | 0.25 | 0.27 | 2.7 | |||||
16 | 16 | 0.64 | 0.64 | 0.64 | 0.13 | 0.34 | 0.25 | 0.27 | 4.1 | |||||
18 | 18 | 0.72 | 0.72 | 0.72 | 0.13 | 0.37 | 0.25 | 0.34 | 5.8 | |||||
20 | 20 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.13 | 0.4 | 0.25 | 0.34 | 8 | |||||
22 | 22 | 0.88 | 0.88 | 0.88 | 0.13 | 0.4 | 0.25 | 0.34 | 10.6 | |||||
24 | 24 | 0.96 | 0.96 | 0.96 | 0.13 | 0.4 | 0.25 | 0.41 | 13.8 | |||||
27 | 27 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 0.13 | 0.4 | 0.25 | 0.41 | 19.7 | |||||
30 | 30 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 0.13 | 0.4 | 0.25 | 0.47 | 27 | |||||
33 | 33 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 0.13 | 0.4 | 0.25 | 0.47 | 35.9 | |||||
36 | 36 | 1.4 | 1.4 | 1.4 | 0.13 | 0.4 | 0.25 | 0.54 | 46.6 | |||||
39 | 39 | 1.6 | 1.6 | 1.6 | 0.13 | 0.4 | 0.25 | 0.54 | 59.3 | |||||
3 檢查與判定程序
驗收檢查程序見GB /T 90。如果表面塗、鍍層影響對表面缺陷的識别,則應在檢查前予以去除。
注: GB /T 90 修訂時将相應删減,以免重複。
3.1 規則
制造者有權采用任何檢查程序,但必須保證產品符合本标準的規定。
需方可以采用本條規定的驗收檢查程序,以确定一批緊固件產品接受或拒收。本程序也适用于有争議時的仲裁檢查, 除非供需雙方在訂單中注明協議的其他驗收程序。
3.2 非破壞性檢查
根據附錄A(标準的附錄)表A1的規定,從驗收批中随機抽取樣本,并進行目測或其他非破壞性的檢查,如磁力技術或渦流電流。若發現有缺陷樣品未超過允許的極限, 則接受該批產品(也見3. 4 條); 若發現有缺陷樣品數超過允許的極限,則這些不合格產品作為批量并按3. 3 條程序繼續進行檢查。
3.3 破壞性檢查
按3.2條的程序,如查出不合格產品,則根據附錄A表A2的規定,将有最嚴重缺陷的產品組成第二樣本,并在通過缺陷的最大深度處取一個垂直于缺陷的截面進行檢查。
3.4 判定
在目測檢查中, 若發現有任何部位上的碎火裂縫或在内拐角上的皺紋或在非圓形軸肩緊固件上有低于支承面超出“三葉”形的皺紋,則拒收該批產品。
在破壞性檢查中,若發現有超出規定允許極限的鍛造裂縫、爆裂、裂絞和條痕、凹痕、切痕或損傷,則拒收該批產品。
Taper keys of keyways

Hexalobular internal driving feature for bolts and screws
Fasteners-Ends of parts with external thread(ISO 4753:2011, MOD)
Fasteners - Bolts, screws and studs - Nominal lengths and thread lengths (ISO 888:2012, MOD)
Countersinks for countersunk head screws
Connections with waisted stud - Tape classification
Flared couplings - Flared end
Hexalobular internal driving feature for bolts and screws
Knurl
Drill diameter for use prior to tapping screw threads
Square and rectangular keyways
Woodruff keyways
General purpose bolts and screws - Radius under the head
Center holes
Rivet Shank Diameters (Except Blind Rivets) [ISO 1051:1999]
Stress area and bearing area for threaded fasteners
Countersunk flat head screws - Part2: Penetration depth of cross recesses
Offset cruciform recess fro rotary fastening devices
Clearance holes for rivets

Hot-rolled channel steel
Hexagon lobuar for fasteners - Type E
Fasteners - Clearanc holes for bolts and screws
Fasteners - Split pin holes and wire holes (ISO 7378:1983)
Countersunk head screws - Head configuration and gauging
Cross recesses for screws
Fastners - Widths across flats of hexagon products
Self-tapping screws for metric ISO threads - Part 2: Guide values for hole diameters
Thread run-outs and thread undercuts
Tapping screw connections - Guideline values for core hole diameters and use
12 point socket for bolts and screws
60° centre holes - Types R. A. B. and C
Thread rolling screws for ISO metric thread guidelinge values for hole diameters
Thread ends and lengths of projection of bolt ends for metric ISO threads according to DIN 13
Knurle
Connections for hydraulic fluid power and general use - Ports and stud ends with ISO 261 metric threads and O-ring sealing - Part 1: Ports with truncated housing for O-ring
Hexalobular internal driving feature for bolts and screws
Connections for general use and fluid power - Ports and stud ends with ISO 228-1 threads with elastomeric or metal-to-metal sealing - Part 1: Threaded ports
Dimensioning and indication of knurling

Fasteners—Ends of parts with external ISO metric thread
Connections for general use and fluid power - Ports and stud ends with ISO 228-1 threads with elastomeric or metal-to-metal sealing - Part 4: Stud ends for general use only with metal-to-metal sealing (type B)
Hexalobular internal driving feature for bolts and screws
Geometrical product specifications (GPS) - Indication of surface texture in technical product documentation

General purpose bolts and screws─Metric series─Radii under the head

Rivet shank diameters
Aerospace - Spline drives - Wrenching configuration - Metric series
Connections for general use and fluid power - Ports and stud ends with ISO 261 threads with elastomeric or metal-to-metal sealing - Part 1: Threaded ports
Connections for general use and fluid power - Ports and stud ends with ISO 261 threads with elastomeric or metal-to-metal sealing - Part 2: Stud ends with elastomeric sealing (type E)
Connections for general use and fluid power - Ports and stud ends with ISO 261 threads with elastomeric or metal-to-metal sealing - Part 3: Stud ends with metal-to-metal sealing (type B)
Connections for general use and fluid power - Ports and stud ends with ISO 725 threads and O-ring sealing - Part 3: Light-duty (L series) stud ends

Fasteners—Surface discontinuities— Part2:Nuts

Countersunk flat hed screws—Part 2:Penetration depth of cross recesses

Fasteners—Surface discontinuities— Part1:Bolts,screws and studs for general requirements
Internal drive, offset cruciform recess (Torq-Set) for rotary fastening devices. Metric series

Fasteners—Thread undercuts for external metric ISO
Cross recessed-H type
Cross recessed-Z type

Countersunk head screws—Head configuration and guaging

Fasteners—Hexagon products—Widths across flats

Fasteners─Clearance holes for bolts and screws

Thread run-out for fasteners with thread in accordance with ISO 261 and ISO 262
Copper tubes of circular section - Dimensions
Hexalobular internal driving feature for bolts and screws
Stress area and bearing area for threaded fasteners
General purpose bolts and screws - Metric series -- Radii under the head
Straight cylindrical involute splines -- side fit -- Generalities, dimensions and inspection
Knurling
Automatic Cold Header - Hole Size
Recess Dimensions for Flat 82° Countersunk Head Screws

Dimensions of Threads and Points for Types BF and BT Thread-Cutting Tapping Screws
Dimensions of Threads and Points for Type D, F, G, and T Thread-Cutting Tapping Screws
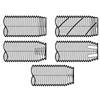
Dimensions of Type TRS Tapping Screws
Standard Test-Plate Thickness and Hole Sizes for Drive-Test Inspection of Tapping Screws
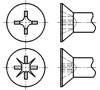
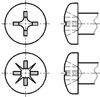
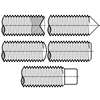
Dimensions of Alternate Styles of Points for Thumb and Wing Screws
Hot rolled flat steel bars and steel wide flats for general purposes - Dimensions and tolerances on shape and dimensions
Cold Rolled Uncoated and Zinc or Zinc-Nickel Electrolytically Coated Low Carbon and High Yield Strength Steel Flat Products for Cold Forming - Tolerances on Dimensions and Shape
Aerospace series - Installation holes for inserts, screw thread, helical coil, self-locking - Design standard
Countersunk head screws - Head configuration and gauging
Tapping rivats - Thread and end
Fasteners - Clearanc holes for bolts and screws
Cross Recesses For Screws
Standard Test-Plate Thickness and Hole Sizes for Drive-Test Inspection of Tapping Screws

Dimensions of Threads and Points for Types BF and BT Thread-Cutting Tapping Screws
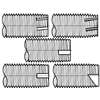
Dimensions of Threads and Points for Type D, F, G, and T Thread-Cutting Tapping Screws
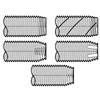
Type TRS Tapping Screws
Dimensions of Hexagon Sockets [Table 18]
![Body and grip lengths for socket head cap screws [Table 4]](https://imgcc.164580.com/upload/48/pic/2021/05/27/1622102178590886964.jpg)
Body and grip lengths for socket head cap screws [Table 4]
Metic threads and points for tapping screws
![Type BF and BT, Thread Cutting Tapping Screws [Table 7]](https://imgcc.164580.com/upload/48/standard/2020/06/05/1591322143016742879.jpg)
Type BF and BT, Thread Cutting Tapping Screws [Table 7]
![Type D,F,G and Type T Thread Cutting Tapping Screws [Table 8]](https://imgcc.164580.com/upload/48/standard/2020/06/05/1591326271806674189.jpg)
Type D,F,G and Type T Thread Cutting Tapping Screws [Table 8]
Aerospace series - Six lobe recess - Dimensions and tolerances
Threaded ends of fitting
